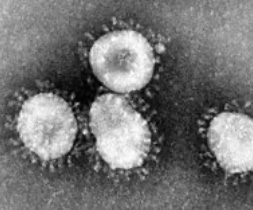
How UV-C works
Healthy buildings are buildings that prioritize the quality of the indoor environment. They bring together data science, machine learning, and best-in-class technology to facilitate connectivity and visibility. These buildings address key criteria, such as air quality and ventilation, to optimize indoor shared spaces.
Did you know humans spend 90% of their lives indoors?
Indoor environments are humans’ natural habitats. We spend 90% of our life indoors,
breathing mostly indoor air up to 20,000 times a day. What are we doing to make our
natural habitats - indoor environments - healthier shared spaces?
There are invisible risks present in indoor environments
As a sustainable solution, UV-C can play a key role in a layered cleaning and
disinfection strategy for achieving indoor environmental quality.
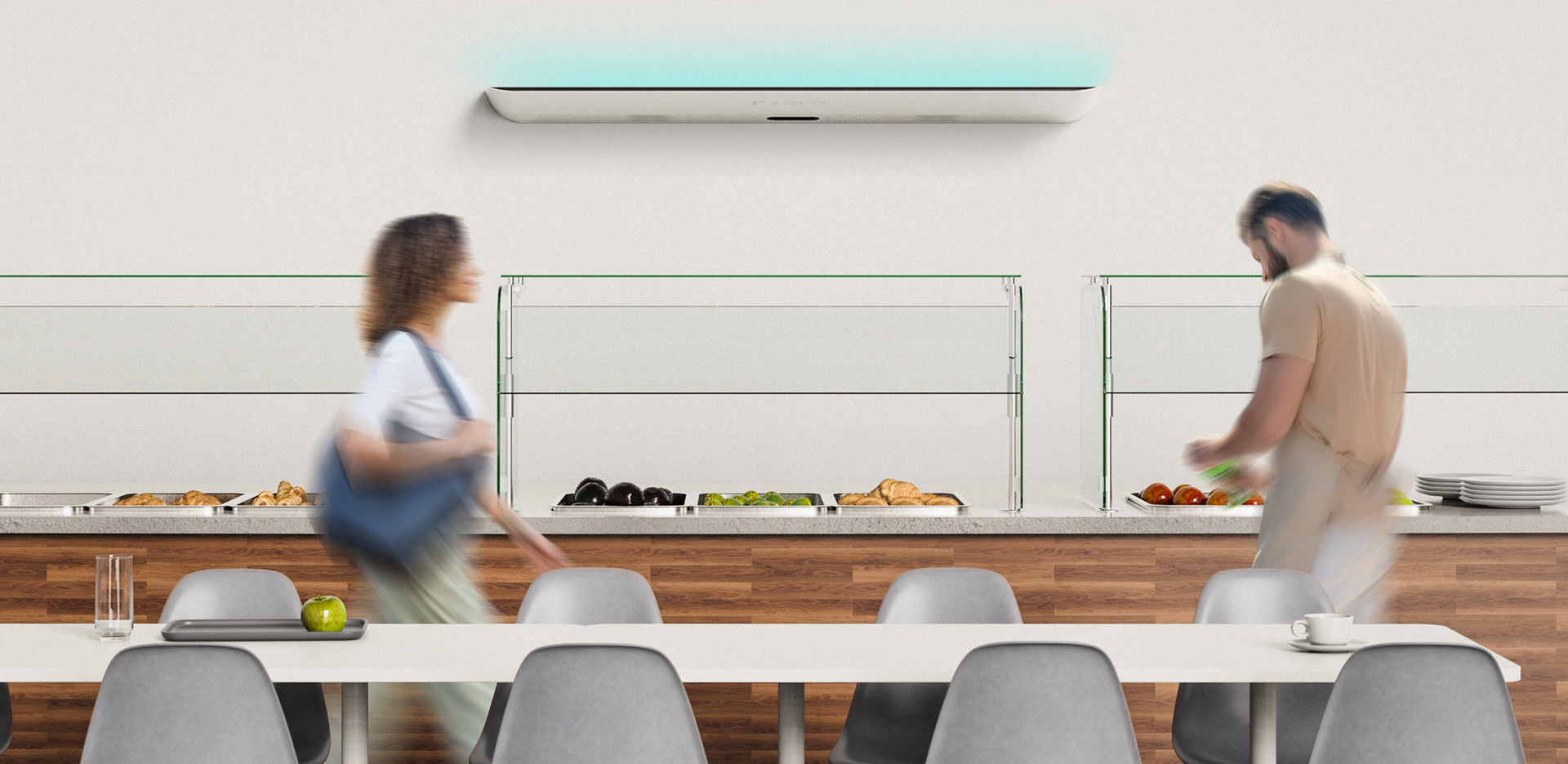

Surfaces
How UV-C works
Ultraviolet (UV) light is light with a wavelength between 10 and 400 nanometers (nm). This light is not visible to the human eye. UV light has three sub-types: UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C.