What is Upper-Room Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI)?
Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI) is a type of UV light used in hospitals and labs since the 1800s to effectively disinfect occupied spaces. It is a type of UV light similar to far-UV light, which we discussed in our last post, but with a few different properties and uses.
As UVGI becomes more accessible for all hospitals, schools, and senior care facilities, it’s important to understand exactly how UVGI works and how it can improve indoor air quality in your space.
What is Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI)?
Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI) uses UV light with wavelengths that are short enough to disinfect air. It irradiates the germs in the light’s path to neutralize both airborne and surface-dwelling microbes. Upper-room UVGI has been used for decades in hospitals and labs to stop the spread of germs.
In contrast to far-UV light, people shouldn’t have prolonged exposure to UVGI, which is why it’s used in an upper-room format that disinfects the space above people’s heads so it will not have contact with skin or eyes.
Why Do We Need UVGI Now?
New mandates by The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) and The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have updated the standards for air circulation in buildings. These standards are measured in Air Changes per Hour (ACH) or equivalent Air Changes per Hour (eACH).
The last time ASHRAE set ventilation standards for buildings was in the 1970s. That standard focused on thermal comfort, the removal of body odor, and energy conservation.
According to the updated standards, the CDC recommends at least 5 eACH for all occupied spaces, while ASHRAE recommends different eACH for different spaces, such as 8.3 eACH for educational spaces and 8 eACH for healthcare exam rooms. However, running the HVAC system at high speeds isn’t the only way to achieve the new targets.
In fact, HVAC systems are designed to promote airflow and temperature control, not disinfection. Your typical HVAC system can achieve between 2 and 4 ACH, and running it at maximum power will run up your buildings’ energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
Upper-room UVGI is designed for the purpose of disinfection and can contribute 10 eACH to a given space without the energy drain or greenhouse gas emission of an overworked HVAC system.
How is UVGI used in Upper-Room Disinfection?
The Process
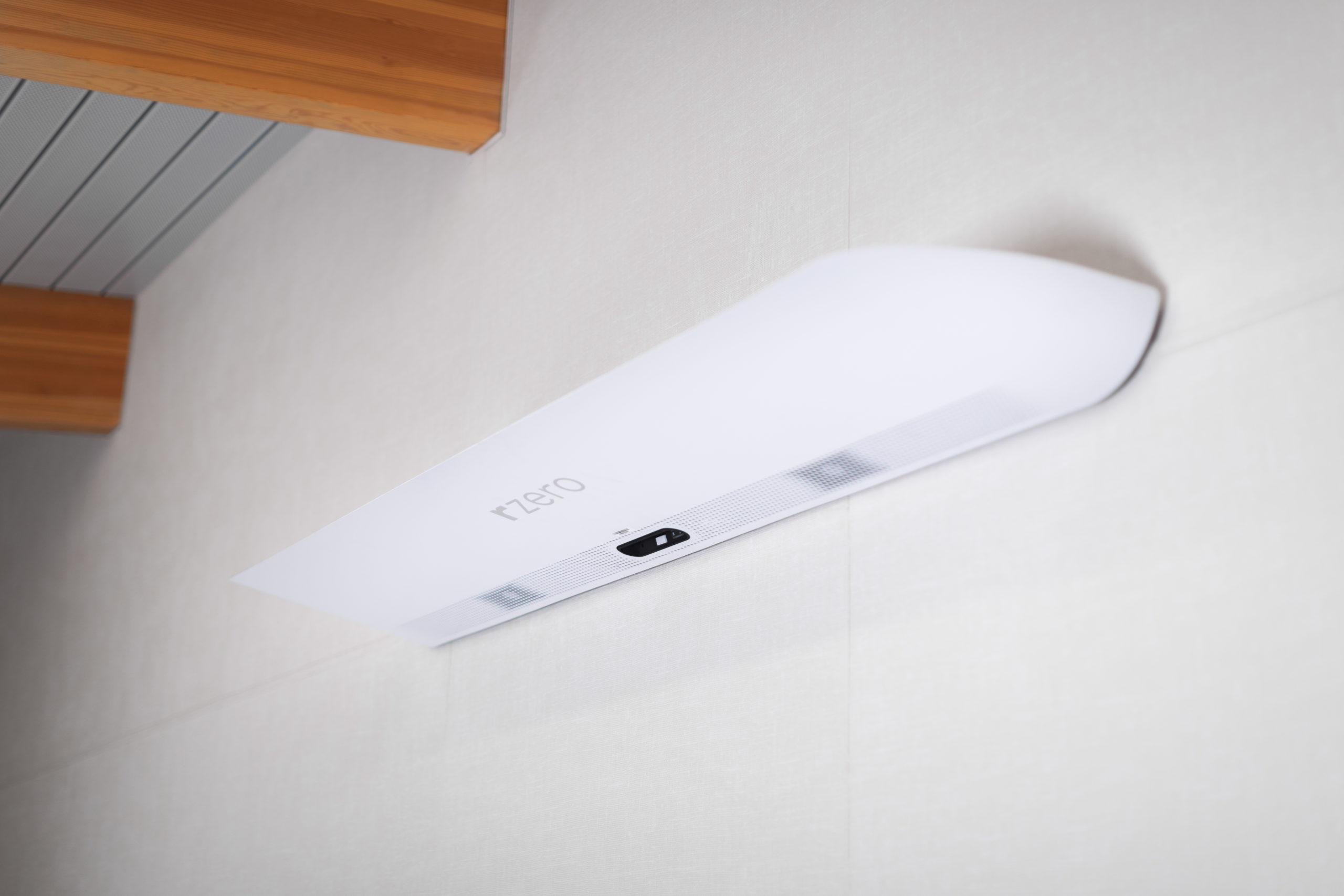
Upper-room Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation is the name for any process that applies UVGI to the upper part of a room, in the space where no person can come into contact with the light. This space is usually 7 feet above the floor to the ceiling.
In R-Zero’s discussion with Dr. Edward Nardell, a physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a professor at the Harvard School of Public Health, he explained the basic process behind upper-room UVGI.
“Upper-room germicidal UV in particular, uses the upper quarter of the room as a large disinfection chamber and virtually instantaneously disinfects that air. And then as the air from the lower room is moved by convection currents and movement and all kinds of other things that happen in rooms, it moves to the upper room and likewise gets quickly disinfected and comes down as purified air.”
Simply put, when people exhale, their breath is warm, which means that their breath – and any infectious particles – will rise to the top of the room. When that breath has reached the top, it will have time to cool and sink again. The UVGI device creates a layer of UV light along the top of the room, and the rising, infectious air is instantly penetrated and deactivated by the UV light.
This cyclical motion of air allows infectious air to constantly rise to the level of UVGI and get deactivated, making sure that the cooled air is safe for people to breathe.
R-Zero’s Beam
R-Zero’s Beam is an upper-room UVGI product that can add up to 12 or more eACH to your space. The ASHRAE standard for healthcare exam rooms is 8 eACH, and the Beam device alone exceeds that expectation. When used in conjunction with an HVAC system that provides 2 ACH, your space could go up to as much as 14+ ACH.
The Beam also supports your building’s goals for energy efficiency and savings since it consumes about as much energy as a high-performance laptop, with 95% less energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions than an HVAC system.
Use Upper-Room UVGI to Keep Your Spaces Safe
Upper-room Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation is a method of air disinfection that uses the principles of air circulation to its advantage. By placing UVGI exactly where exhaled air rises, you can maintain the recommended number of eACH in occupied spaces, affordably.
Are you ready to see how UVGI devices can disinfect your space? Contact us today to find out how to increase your eACH.
More posts you might like
-

3 Key Takeaways from AHR Expo 2025: What’s Shaping the Future of HVAC
The 2025 AHR Expo brought together HVAC industry leaders, innovators, and professionals to showcase the latest advancements in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. Here are the key insights that stood out from our team on the ground. 1. Smart Technology is Enhancing, Not Replacing, Traditional HVAC A significant shift observed at this year’s expo is […]
-

Webinar Recap: Redefining Energy Efficiency
As commercial energy costs continue to rise, building operators are looking for faster, cost-effective solutions to reduce waste and improve efficiency. Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems account for nearly 60-70% of total building energy consumption, making them one of the largest opportunities for savings. However, traditional HVAC systems often operate on outdated schedules, […]
-
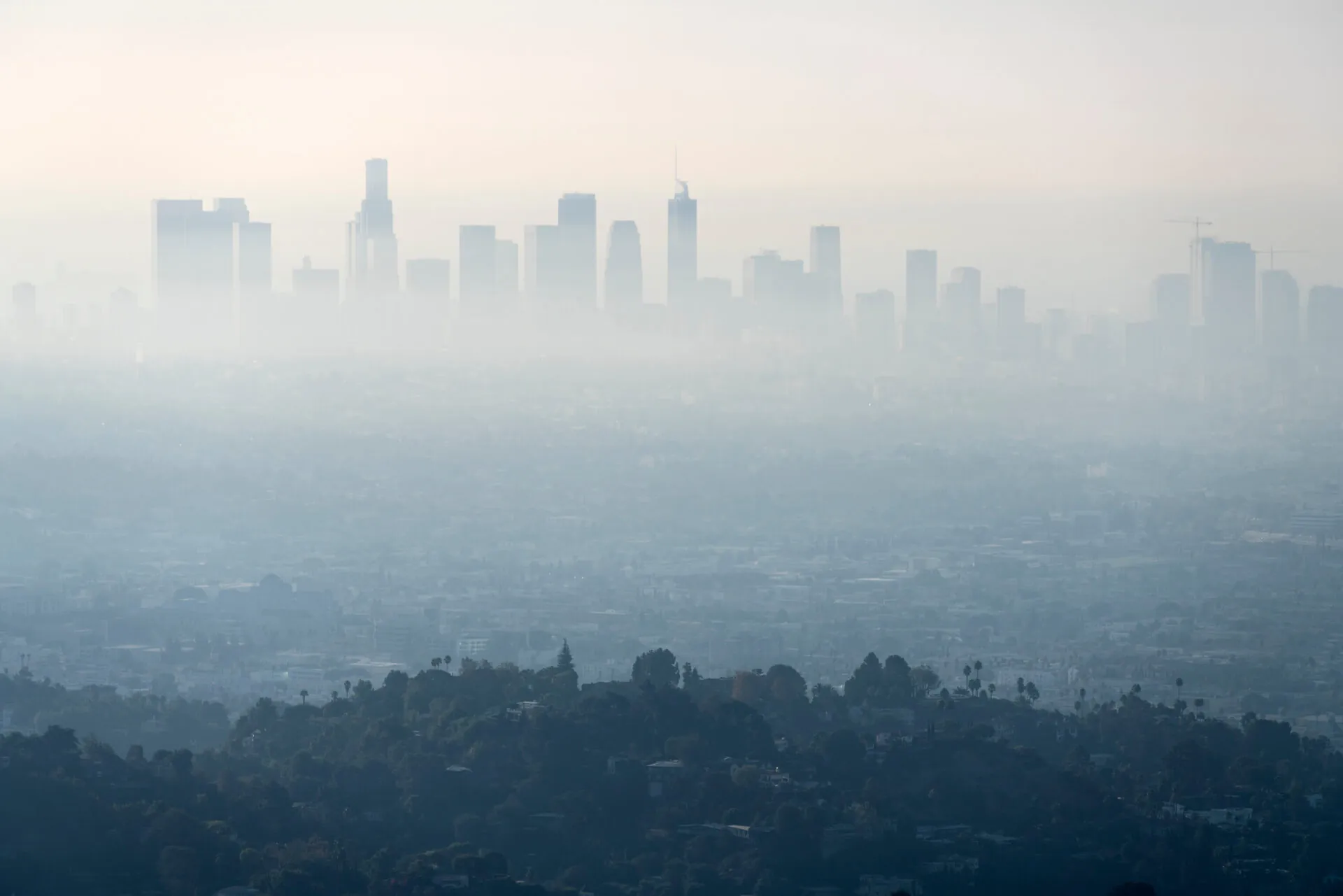

Wildfire Smoke: Understanding the Impact on Indoor Air Quality
As we face yet another intense wildfire season, with significant events already impacting regions across the country, the challenges to air quality, both outdoors and indoors, are more pressing than ever. Wildfires contribute up to 50% of “ultrafine” particles in the air; tiny pollutants that can travel hundreds of miles and infiltrate indoor spaces, affecting […]